Laboratory rotavaporator, what are its applications
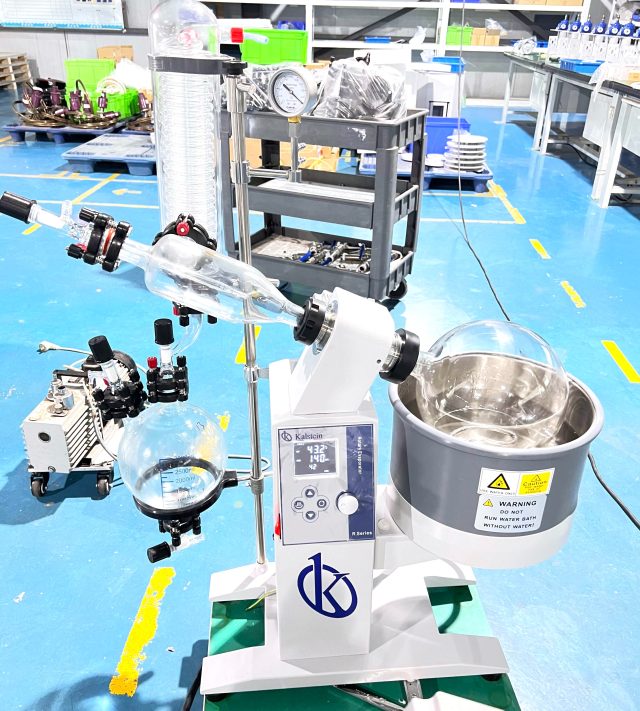

It is a necessary equipment to separate a solvent from asample, through distillation, and then recondense them to separate basic components from each other; this rotary distillation instrument associated with a water bath performs fractional distillations, it is mainly used to separate by means of evaporation at reduced and soft pressure the solvent that accompanies the solute of interest.
Laboratory homogenizer, what are the different types?
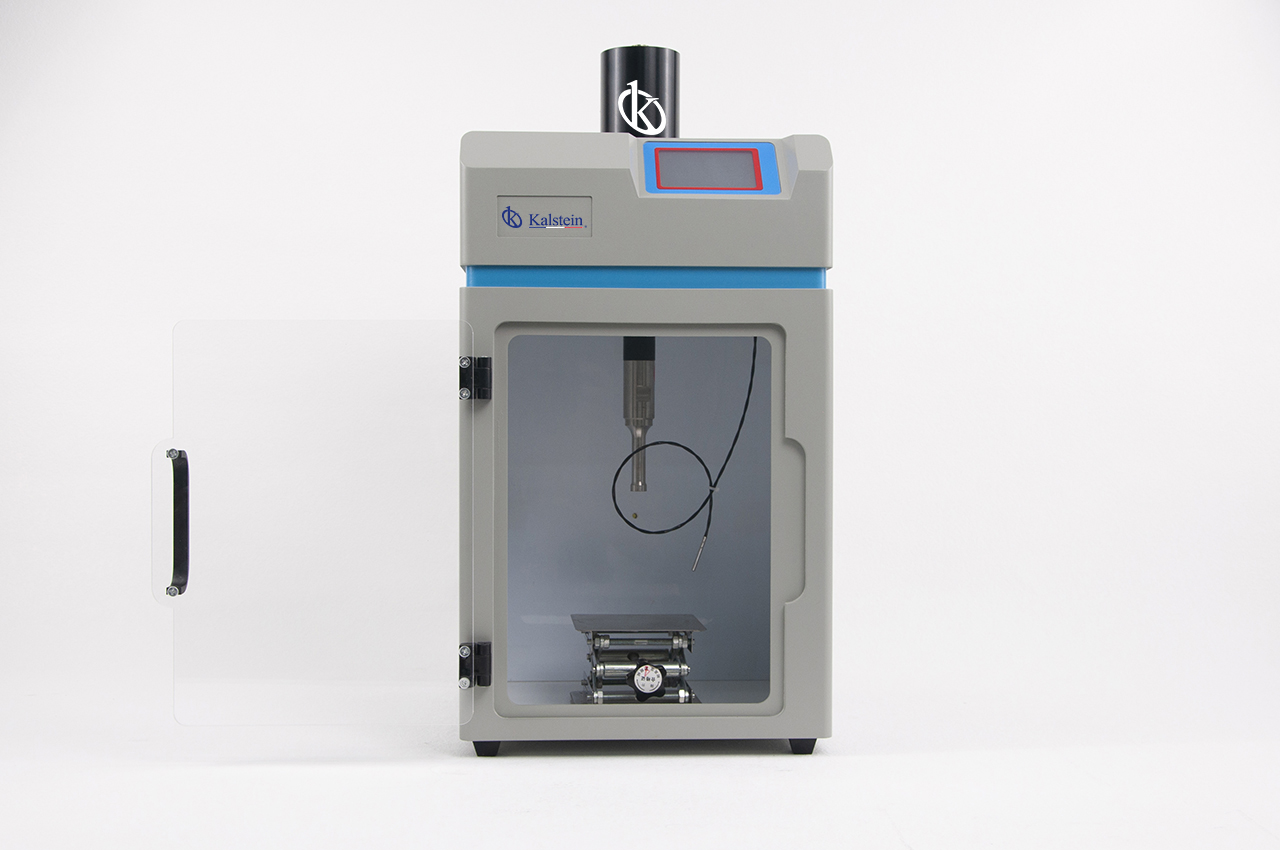

A homogenizer is a laboratory equipment that is used to carry out the homogenization process of different types of materials; such as tissues, food, plants and other biological or chemical elements. In laboratories, homogenization is generally a necessary step in the preparation of biological samples in laboratories, among them we can mention before the analysis of nucleic acids and proteins, or the study of cells, metabolism, bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses. as well as in other scientific purposes.
Laboratory pipettes, which are the main brands?

Pipettes are indispensable products to carry out the development work of a laboratory, to handle chemical, toxic, reactive agents or biological material; to carry out these tasks we need the best equipment, but also the best prices and quality; so KALSTEIN offers you a list of the best brands of laboratory pipettes, classified according to their quality and that suits your needs.
Electrophoresis Applications
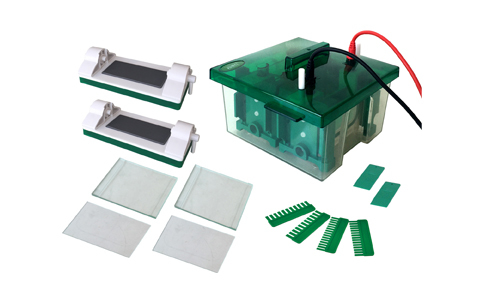
Electrophoresis is a laboratory technique in which a controlled electric current is used in order to separate biomolecules according to their size and electric charge through a porous matrix. Among the main applications of electrophoresis we can mention:
Electrophoresis Power Sources: How does it work?

A power source for electrophoresis is the source that manages constant and direct current to the electrophoresis system, as well as indicates and allows us to control both the supply voltage and the current consumption. In other words, this device provides the necessary energy for this system to function properly; and this important laboratory technique can be carried out.
Parts of a microscope
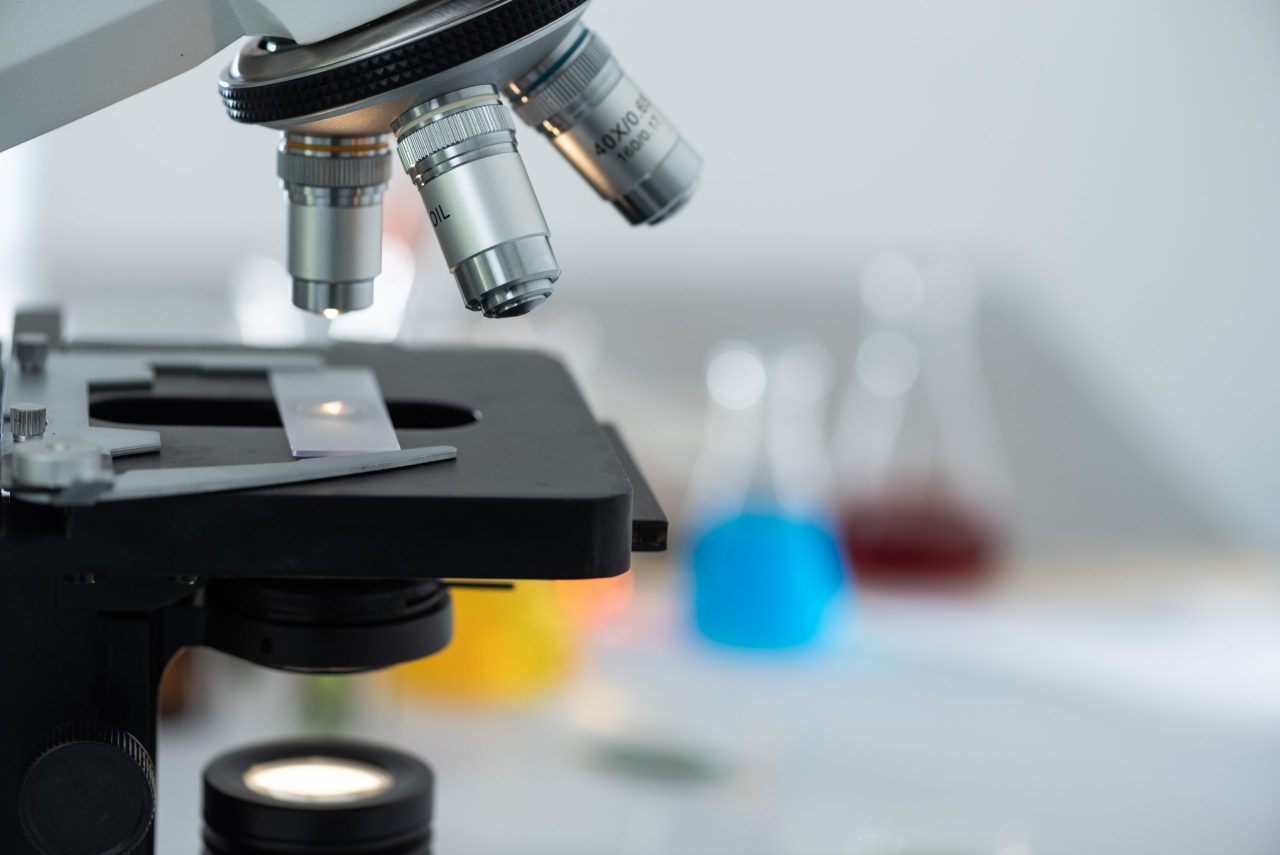

The microscope is a piece of equipment that has been evolving day by day thanks to advances in its electronic and mechanical optical components. The knowledge of the fundamental structure of a microscope and the parts that compose it as well as its function, will help the user in his interrelation with the microscopic equipment to make the appropriate decisions about the necessary care of the same.
Turbidimeter vs. Spectrophotometer
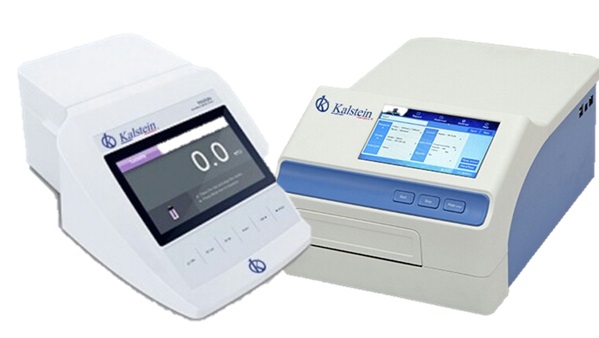
A turbidimeter is a laboratory equipment, portable or benchtop, that is used to measure the turbidity of a liquid. These devices can also set the size and concentration of suspended particles through light scattering in a tube.
What is a tissue processor in pathology?
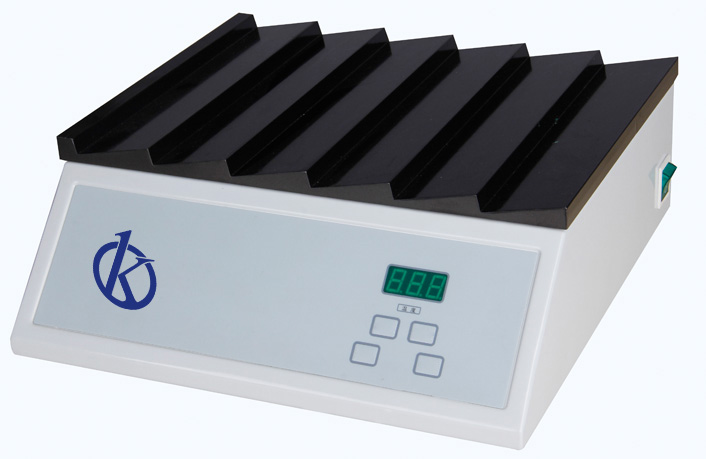

Pathological anatomy is the science that is responsible for the study of pathophysiological and morphological alterations of the disease. Like all science, it has a series of specialized equipment to carry out the different studies on which it is based.
Uses in a laboratory of the “Ice Maker”
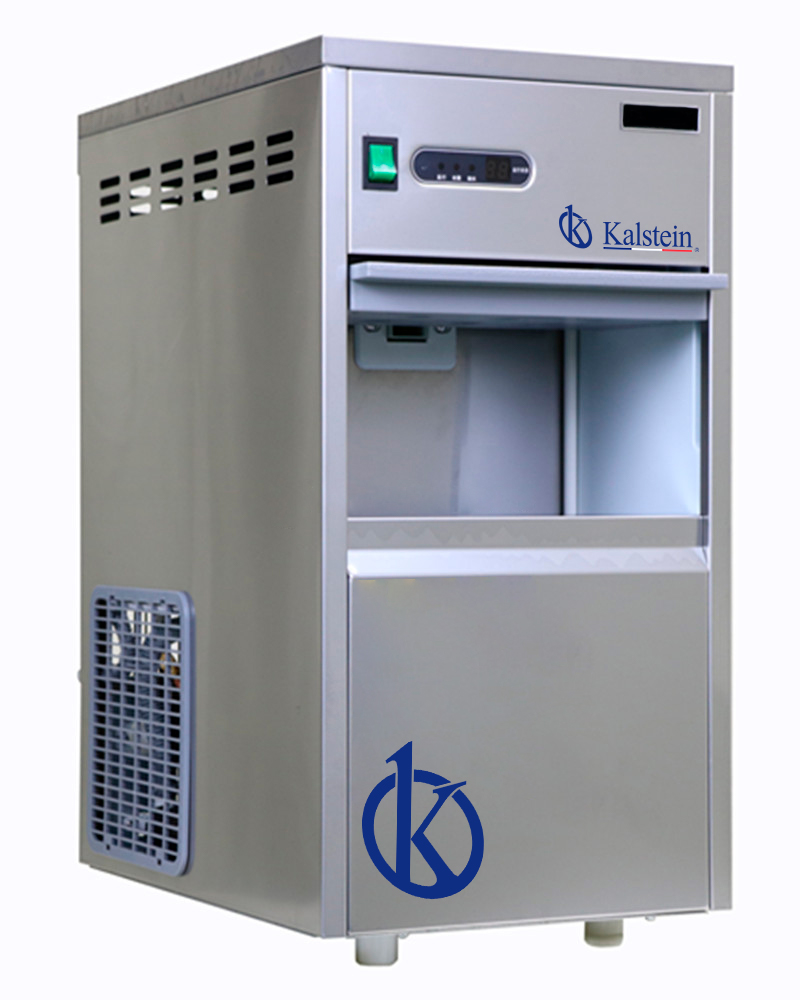

An ice maker is a machine for making ice. This machine produces the ice from moving water, the difference from the traditional method of making ice, where the water is frozen. This principle results in the air being removed, as well as the suspended solids.
Reverse osmosis and water purification
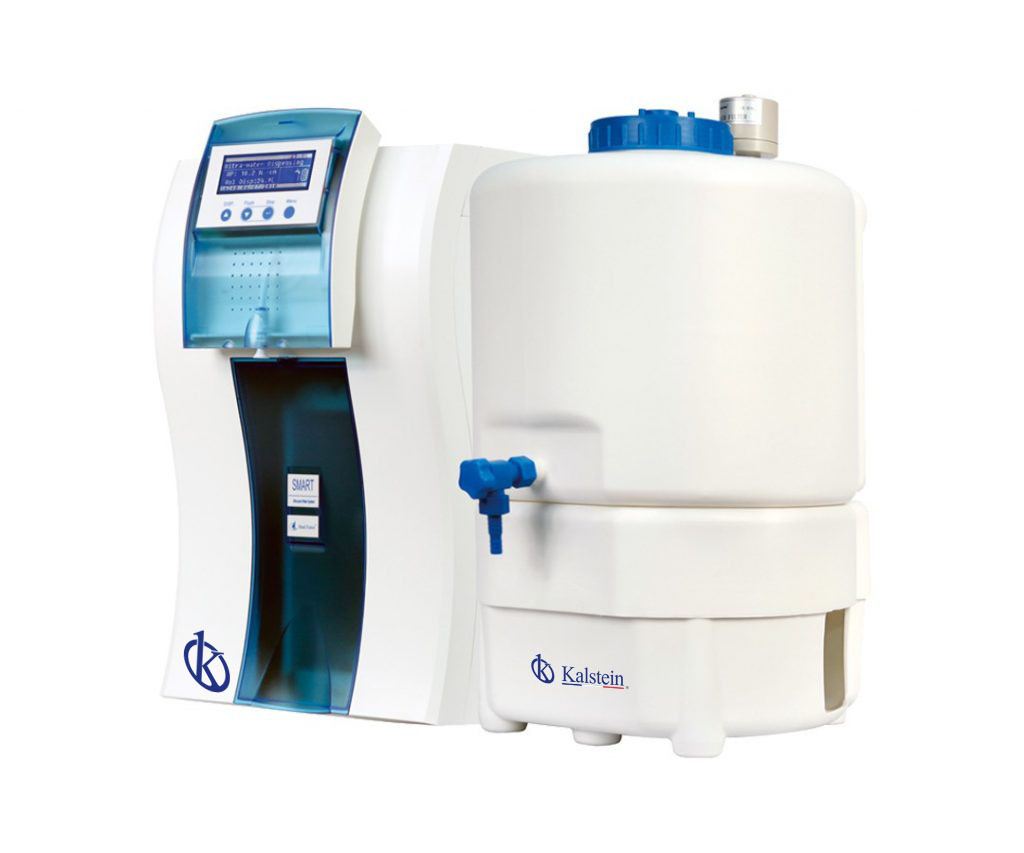

The purification of drinking water consists of a series of steps to which the water is subjected to eliminate waste (solid and mineral) and microorganisms from it in order to obtain water of greater purity and better quality for the consumer.
