Is a child radiant heater important?
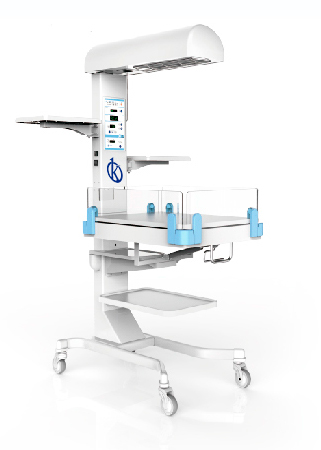
A child radiant heater is a unit used to provide radiant heat to newborns in a comfortable thermal area that maintains their body temperature from 36 to 37 degrees. Newborns who are placed in radiant heaters are usually premature or low birth weight patients who have thermo-regulation problems and are therefore unable to maintain thermal balance, and newborns who may present some critical condition that require constant intervention by medical personnel.
Patient Monitor: How should it be interpreted?
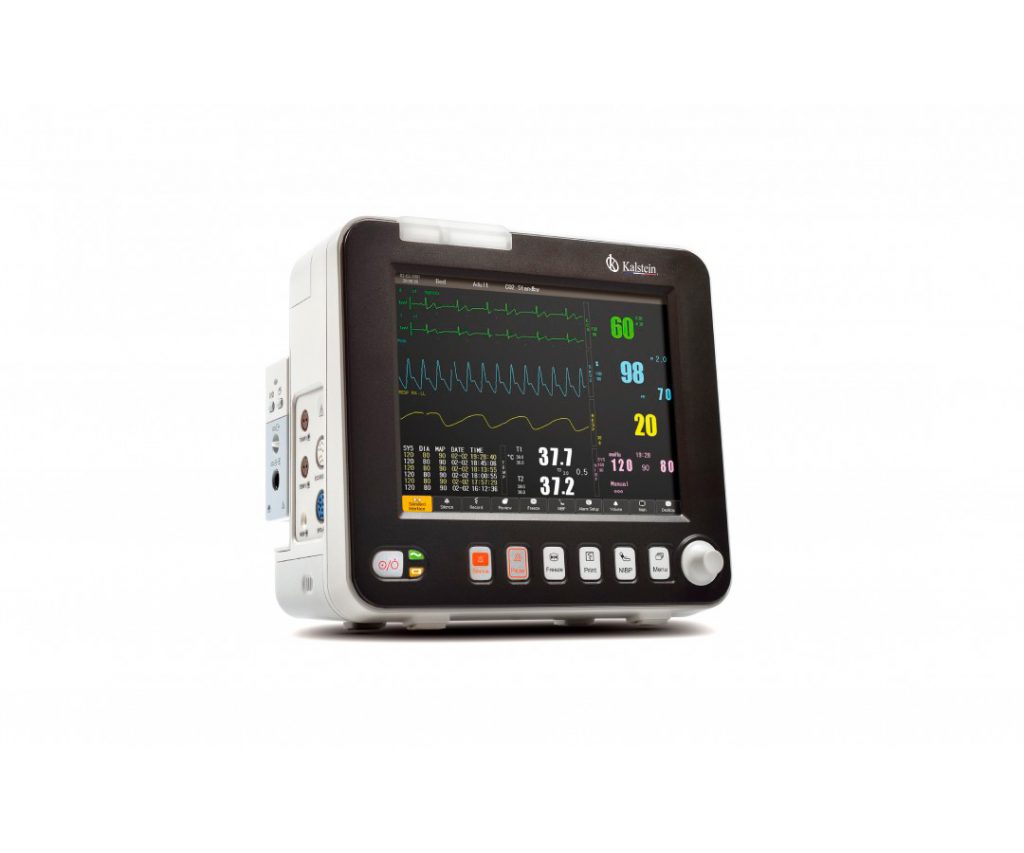
A patient monitor is a medical device that allows monitoring the vital signs of patients in critical condition and should be subjected to constant surveillance by medical personnel, in case of any alteration in the values of these; vital signs that are recorded with this equipment are: heart rate (ECG), respiratory rate (RESP), non-invasive blood pressure (NIBP), pulse (PR), oxygen saturation (SpO2), temperature (TEM), CO2 and invasive blood pressure (PAI).
How are infusion pumps classified?
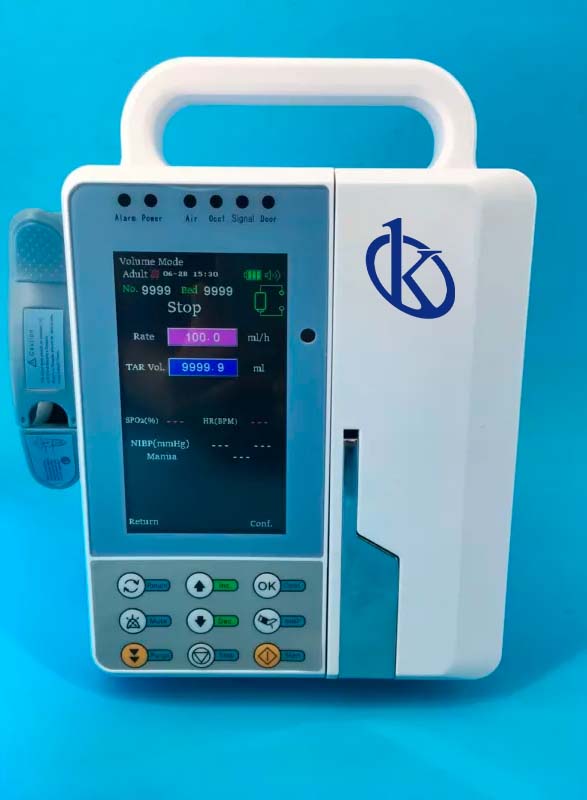
These devices are part of the medical line, they use artificial energy able to provide a positive pressure to the liquid to infuse accurately and safely in the infusion of drugs under strict flow control, one of its characteristics is that they exceed small occlusion pressures and resistance that oppose the infusion antibacterial filters and arterial lines, in addition they can infuse drugs with great precision at very low speeds.
Laboratory biosecurity cabinets: When should they be used?

Biological safety Cabinets are laboratory equipment that acts as ventilated enclosures designed to protect the operator, laboratory atmosphere and working materials from exposure to infectious spatter or aerosols that may be generated by handling material containing infectious agents. This means that laboratory equipment must be used when working with certain microorganisms, cytotoxic products or products that cause allergic reactions.
What are the different types of children’s heaters?

Childhood heaters are medical equipment designed to provide constant heat to low-weight newborns who have thermoregulation problems or who need constant interventions by medical staff, as their purpose is to maintain a temperature-controlled environment to help newborns maintain their body temperature.
Laboratory Shaker: What are its uses and importance?
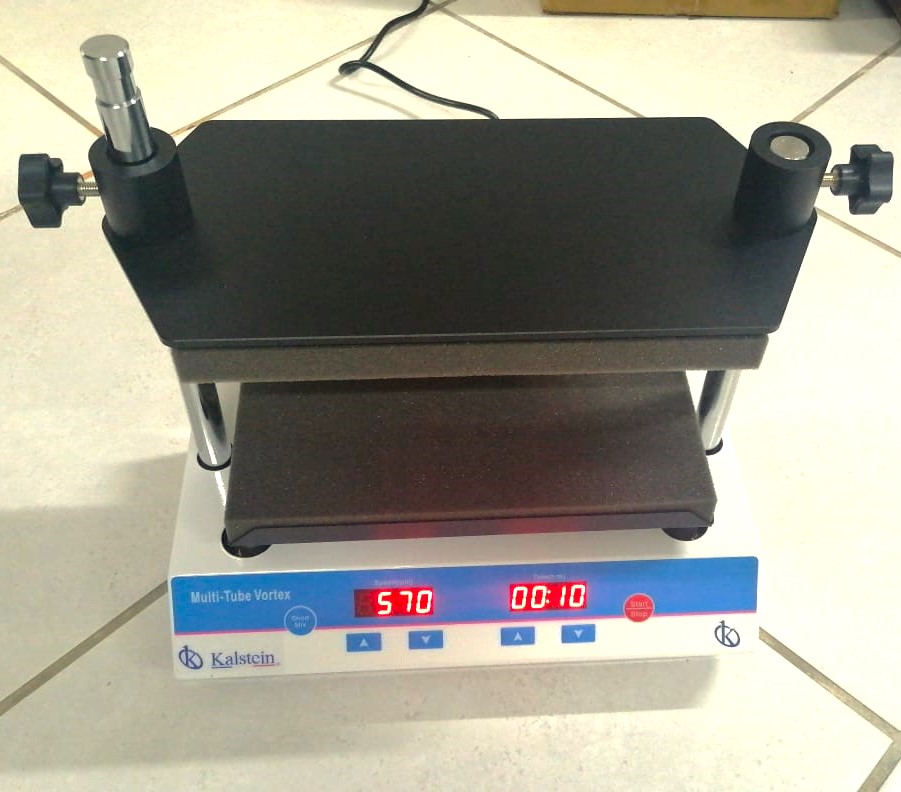

An agitator is an instrument for use by laboratories mostly of chemistry and biology, it is used to mix solutions or preparations, suspensions, these liquids that are going to make mixed or agitated are placed in vessels, tubes or flasks, since its beginnings the manual agitator fulfilled the function of mixing liquids, with technological advances the agitator systems are used in all scientific laboratories, industrial, chemistry, biology, among others.
Infusion pumps: what are they and what are they used for?
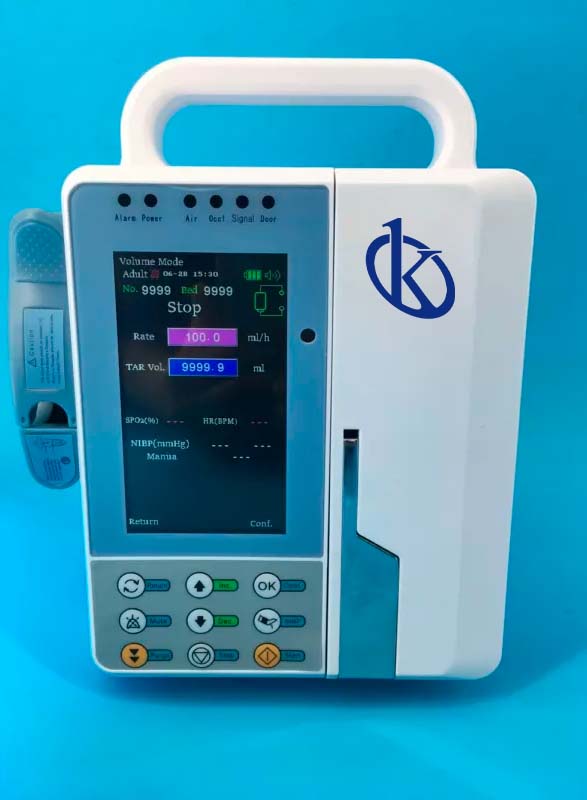
These medical equipment are the precise solution to fluid administration in the patient, since the infusion pumps were introduced in hospitals and clinics, precision errors have been reduced avoiding delays in patient recovery or possible complications that may arise in the administration of treatment to the patient; in addition to allowing the nurse to perform other activities because she should no longer be constantly monitoring the administration of fluids.
Turbidimeter or turbidity meter. How should it be used?
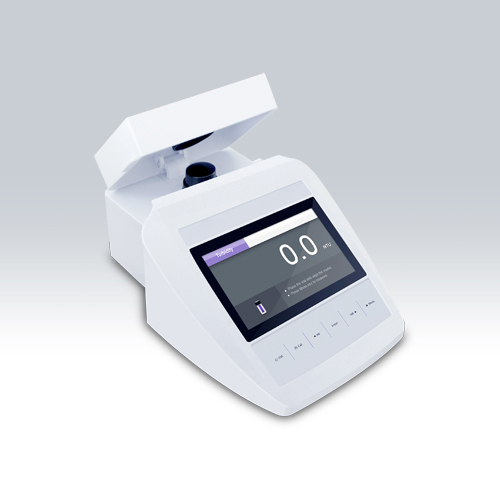

A turbidimeter is a device that allows evaluating how cloudy a liquid is, that is, it determines the turbidity. It does this through an optical analysis that allows it to measure the particles in suspension in a dissolved gas or in a liquid. For which it uses a light source and a light detector (a photocell) set at right angles to the original beam.
Thermocycler: How many types are there?
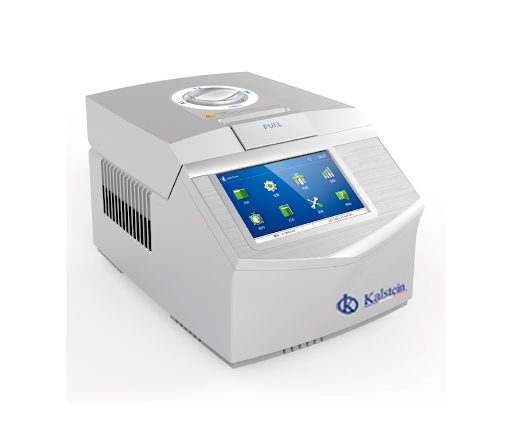

The thermocycler is a laboratory molecular biology team that allows the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) efficiently and quickly, by performing automatic and cyclic temperature changes required for the amplification of a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) chain, from a thermostable enzyme. The PCR technique allows a small amount of DNA molecules to be amplified many times, exponentially.
Hematology analyzers and biochemistry analyzers: what are the differences?
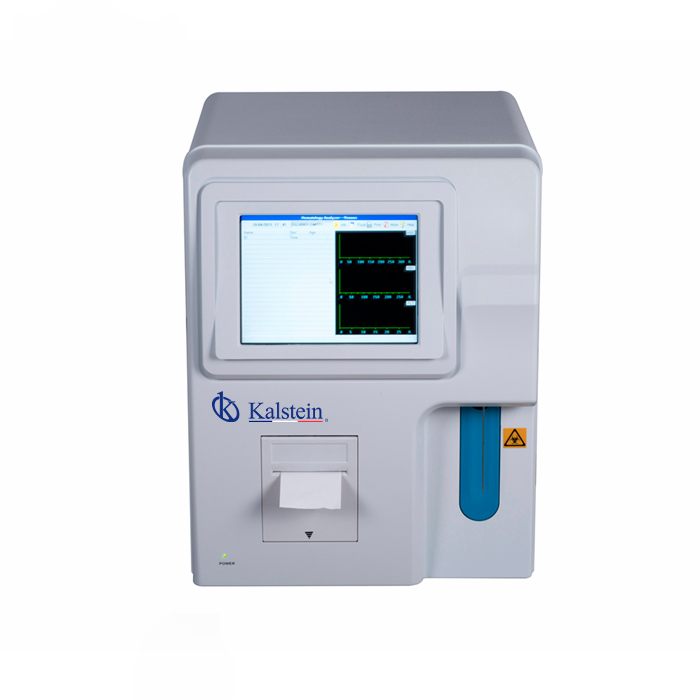
The differences between these teams are mainly focused on their applications, being hematology analyzers devices used for tests involving complete blood counts or blood counts, providing a quantitative and qualitative analysis of blood elements; for biochemical analyzers are used to determine metabolites that are present in biological samples, they can be blood or urine.
