Laboratory Incubators: How Do They Work?
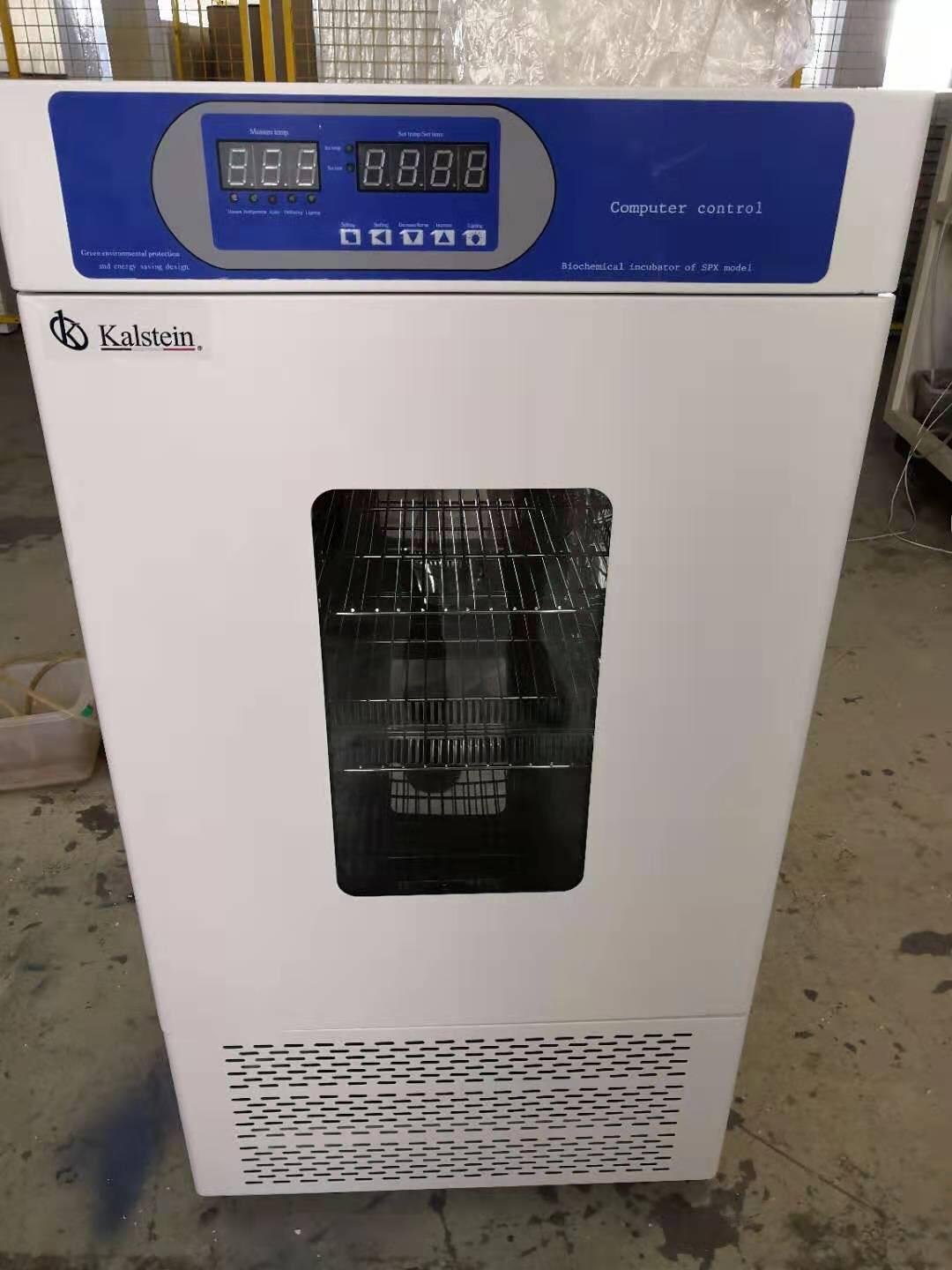

An incubator is a laboratory equipment that allows to carry out a large amount of experimental work, because with it microbiological and cell cultures can be maintained thanks to its ability to achieve the optimum temperature and humidity for it, as well as the levels carbon dioxide and oxygen.
What is a Microwave Digester?
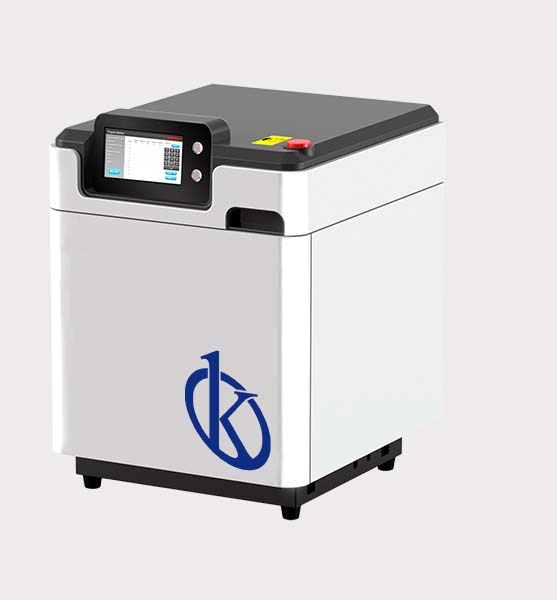

They are equipment that have a digestion system, which is used to mineralize the solid samples from which we want to obtain reliable information at elemental level, a spectroscopic technique is used, and requires that the sample to be examined is in liquid state, so if the requirements of the analyzes require preparing the sample for analyzes of food, textiles, dishes, wastewater treatments, cosmetics and other applications, you need a microwave digester, and undoubtedly the best and most reliable are the YR KALSTEIN series.
Microwave Digester: how does it work?
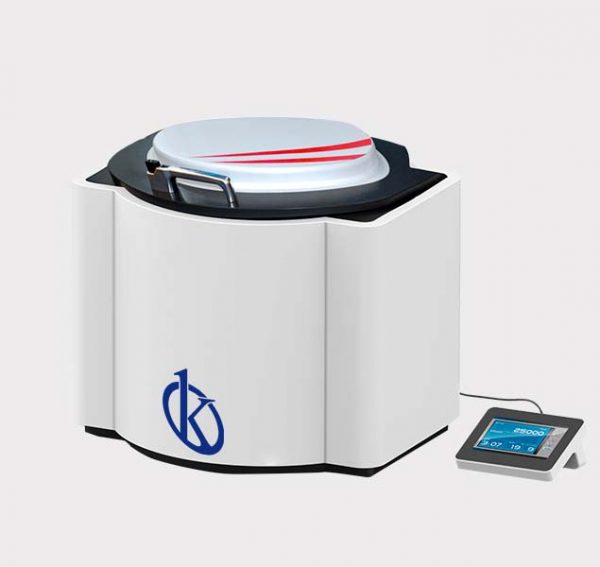

This equipment guarantees the preparation of samples for elemental analysis in analytical chemistry, performs a procedure where electromagnetic radiation is produced at a frequency of 2450 MHz; this makes it warm, where radiation penetrates glass, ceramic and plastic materials, while metals reflect this wavelength.
What is an APL valve?
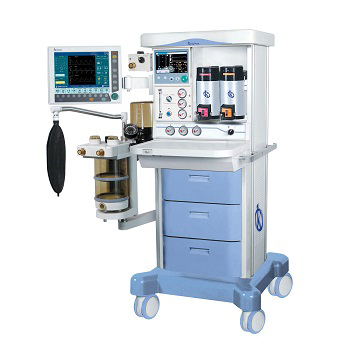
The pressure limitation valve, known by its acronym (APL), is a device that controls the distribution in the release of anesthetic gases, establishes pressure limits for manual ventilation in the breathing circuit by means of a diaphragm. The gases flow from the patient to the scanning system via the APL valve, where pressure fluctuates regularly.
How effective can a phototherapy unit be for the skin?
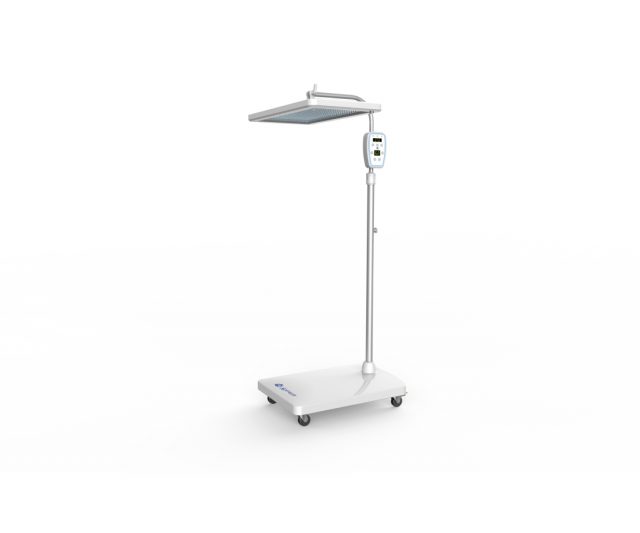

Phototherapy is a dermatological technique and also used in other areas of medicine, where ultraviolet light (UV) radiation is used for the treatment of skin or skin diseases. Thanks to the anti-inflammatory action, it possesses UV radiation, allowing the treatment of inflammatory dermatological and neoplastic skin diseases.
What is jaundice? How is it treated?

Jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes caused by the accumulation or deposition of bilirubin. In newborns, the pathological increase in bilirubin is most often secondary to the destruction or lysis of red blood cells, since the concentration of these cells is higher in the fetus in order to make better use of the scarce amount of oxygen available in the uterine interior.
What is thermofusion?
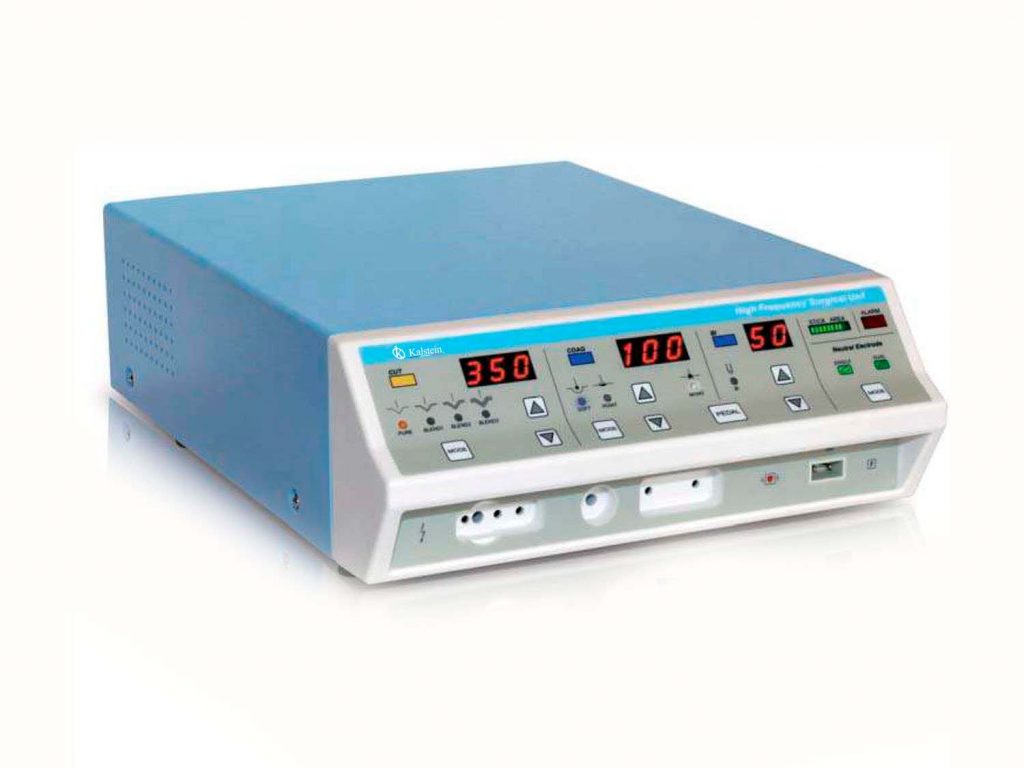

Vascular thermofusion or sealing refers to the process used in electrosurgery to seal blood vessels and tissue bundles before tissue section, fusing collagen and elastin from vascular walls and generating an autologous and permanent sealing, which allows for blood vessels with a diameter less than 7 mm no staples, or sutures, because thermofusion provides protection against possible recurrent bleeding.
Surgical navigation systems optics and cancer
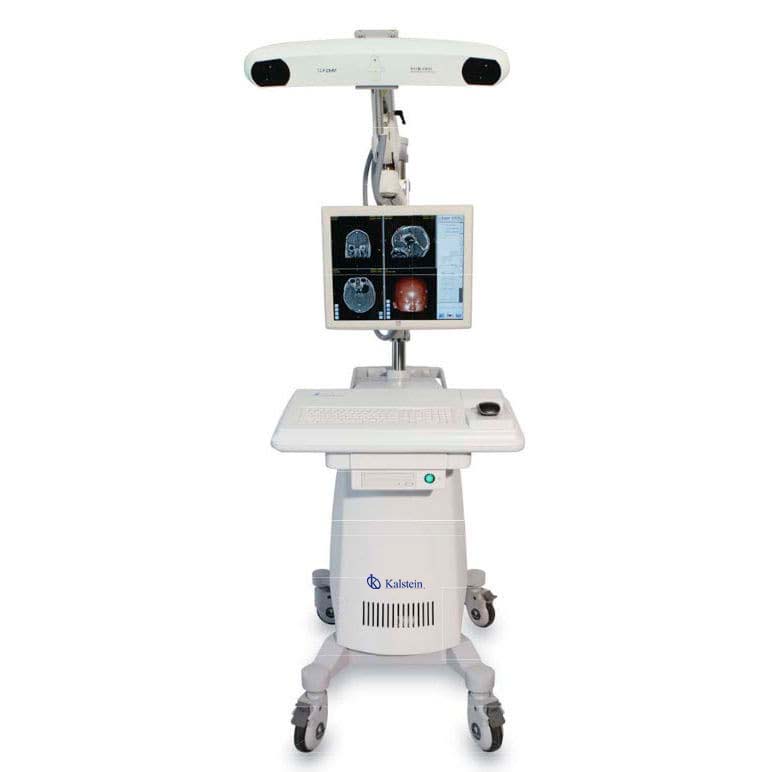
According to the functions of the optical surgical navigation, it allows the detection of cancer in patients, also decreases the arrival times to the specialist of the patient, by means of guidance to identify and overcome the barriers that face and prevent early detection, as well as adequate and timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease. In addition, health experts achieve levels of accuracy and security in image acquisition, which are extended and assisted by computer, magnifying images, facilitating diagnosis, planning and execution of procedures.
Who prepares the operating table?
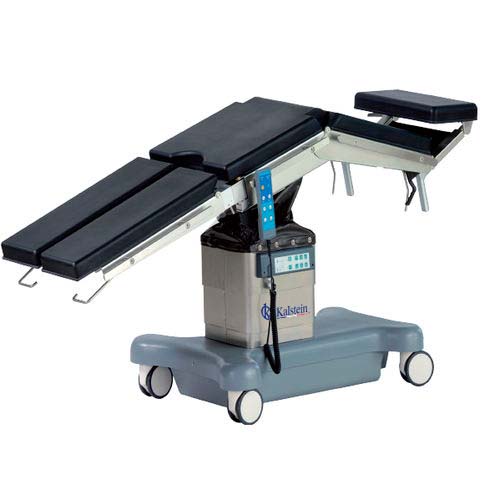

The player inside the operating room plays an important and essential role; its training must be constant and in accordance with the advances of medical technology, and must be marked by a strong technical but also ethical element.
What is anesthesia and how is it applied?
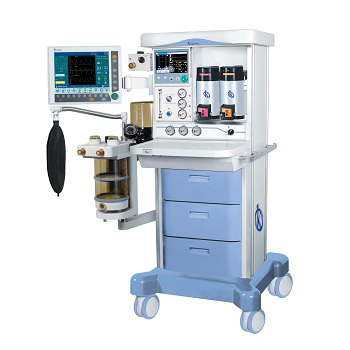
Anesthesia is used to avoid pain in patients during a surgical process and other procedures. They are applied during minor interventions, such as repairing a tooth, during the process of a delivery or colonoscopies. It is also used, during minor and major operations, in some cases, a dentist, nurse or doctor may give you an anesthetic. In other cases, you may need an anesthesiologist, a doctor who specializes in administering anesthesia.
