For use with a portable ultrasound scanner?
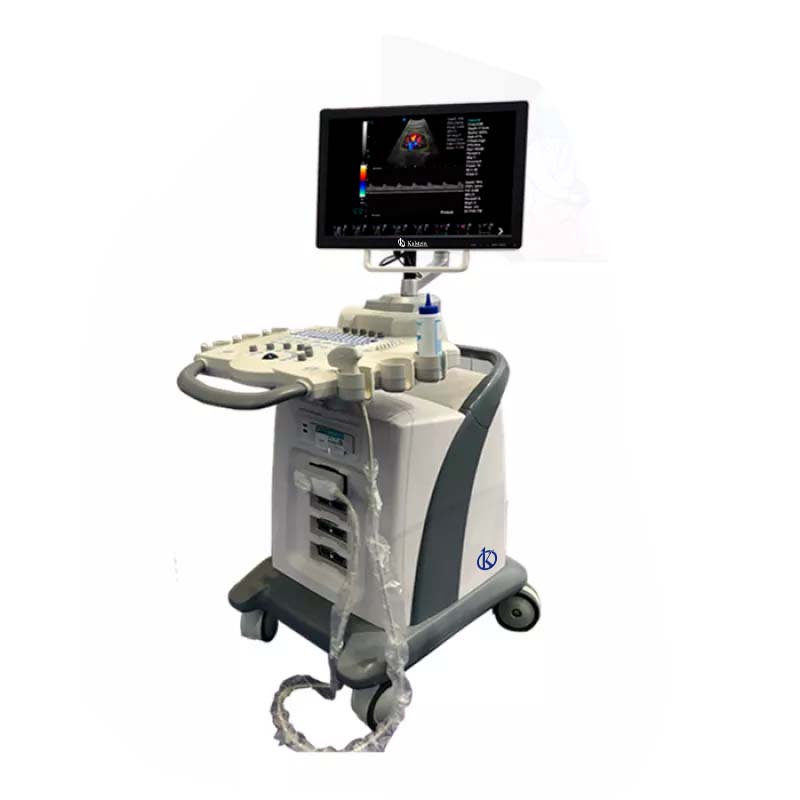
This handheld ultrasound device is small and very low cost, has as advantages that makes ultrasound more simple, also allows you to be everywhere inside the hospital, facilitating the doctor’s tour of the patient’s body; it is used in a variety of applications in different departments, the widest for a single ultrasound probe, making it an imaging device for the whole body, in urological, abdominal, fetal, cardiovascular, gynecological and musculoskeletal applications, among others.
Care and maintenance of an electrocardiograph

An electrocardiograph is a medical device that analyzes the electrical mechanisms of the heart over a period of time. It works in conjunction with electrodes placed on the patient’s chest and limbs to detect electrical changes.
What are the differences between a mono channel and multichannel electrocardiograph?
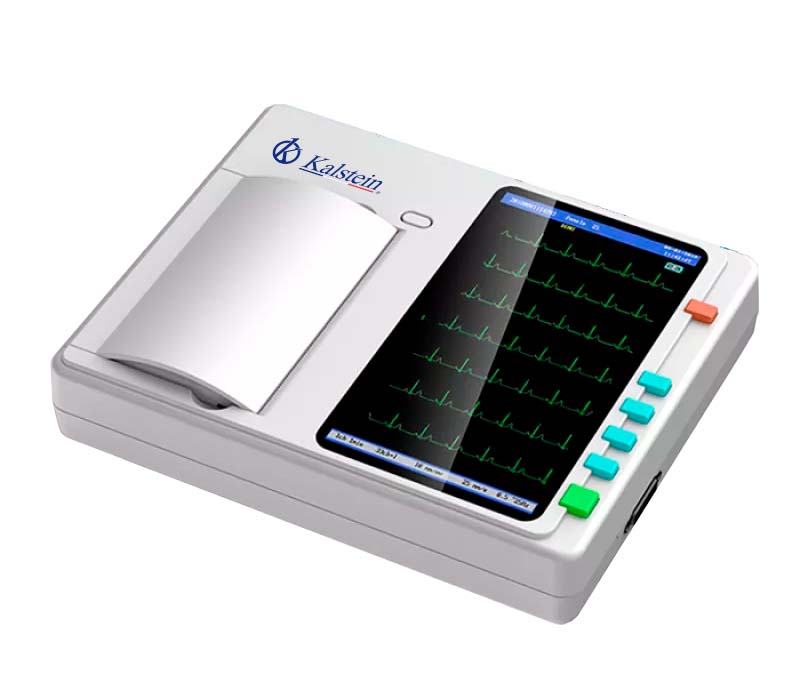
The electrocardiograph is a medical team in charge of performing tests called electrocardiogram (ECD), and detect the signals of the heart, and in turn, to diagnose some of the diseases of the heart. This device is essential in all health centers, especially in cardiology units.
What does an electrocardiograph represent?
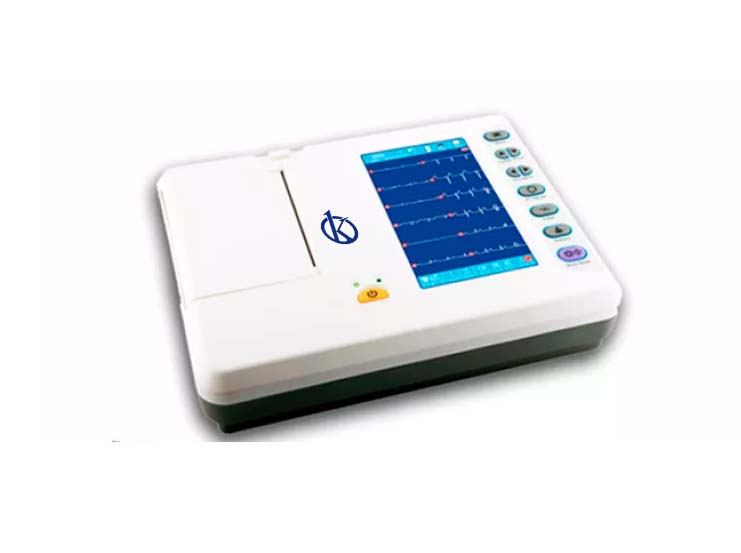
This device that captures and expands the electrical activity of the heart through electrodes, this device represents the electrical activity of myocardial fibers, produced when cardiac muscles change their electrical properties with each beat, then electrodes attached to the body can be used, to measure changes in the body’s voltage, and this is called electrocardiogram.
What Is A Single-Channel Electrocardiograph?
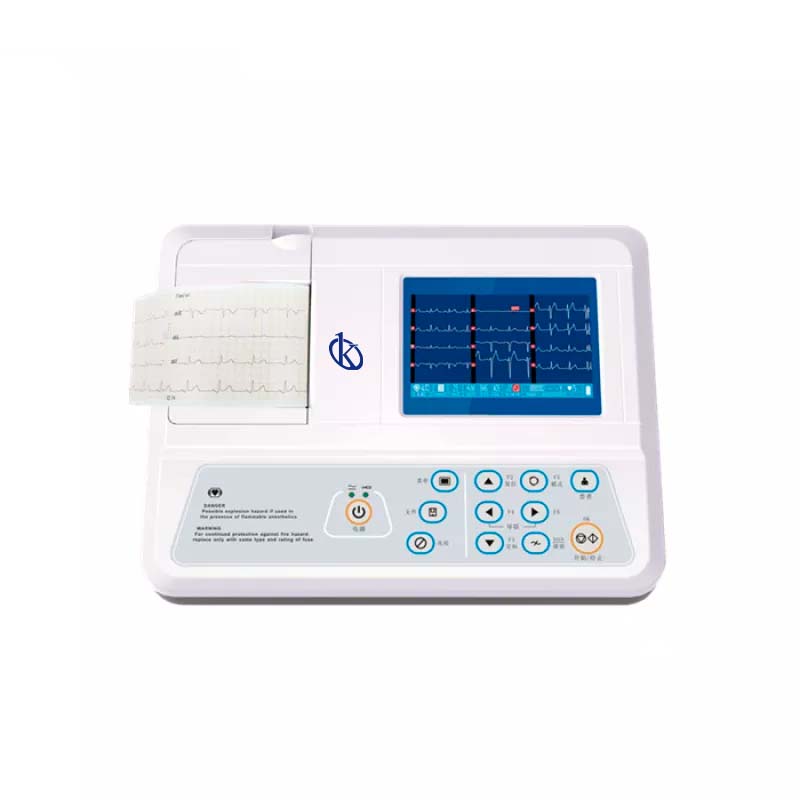
They are medical equipment that records and prints the electrical impulses of the heart automatically and in a selected sequence. The operator selects the automatic or manual change, the chart speed, the signal sensitivity and the response range. So, from the manual mode the operator selects the cables that will be recorded and the equipment tracks the signal to perform the study. On the other hand, it automatically selects the analysis window related to the recording time for each derivation, and the unit automatically records what is scheduled. Also, for 2.5 seconds, the machine tracks 12 leads in a standard way recorded in one strip per rhythm.
What are the Applications of Muffles in a Laboratory?

The use of muffles in laboratories, are furnaces capable of heating at high temperatures, ceramic materials, drying and incinerating substances and products. To do this, muffles are used, a type of oven intended to reach temperatures above 200ºC
Why is a Muffle important in a Chemistry Laboratory?

There are several wonderful instruments and equipment, such as the studies that are carried out in them. There is every prototype and with many benefits, which are used according to the needs. One of the areas in which chemistry laboratory equipment is mostly used is sterilization.
What are the areas of a pathology laboratory?

The pathology laboratory is a specialized medical service that is responsible for receiving histological samples to be processed and analyzed by highly qualified professionals to issue an accurate diagnosis, in addition to providing a series of variables that are prognostic and predictive factors for the treatment of different diseases.
What are the regulations for a safety cabinet?
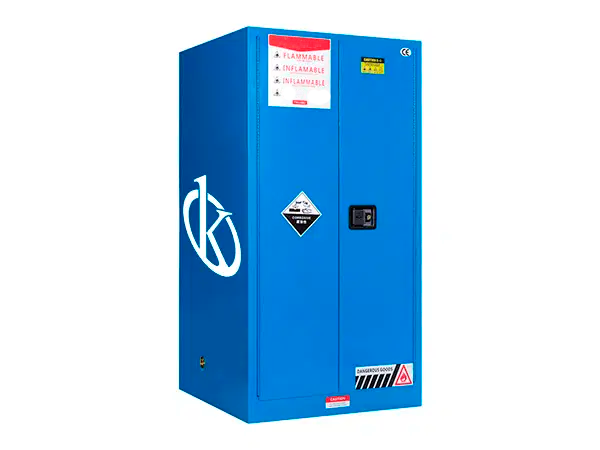

A safety cabinet is prefabricated equipment specially designed to carry out the storage of hazardous chemicals in mobile containers protecting their contents in case of fire, for a certain period of time and which meets the safety requirements of this ITC (International Trade Center) and the APQ Regulation (656/2017).
What are the steps to use and calibrate a turbidimeter?
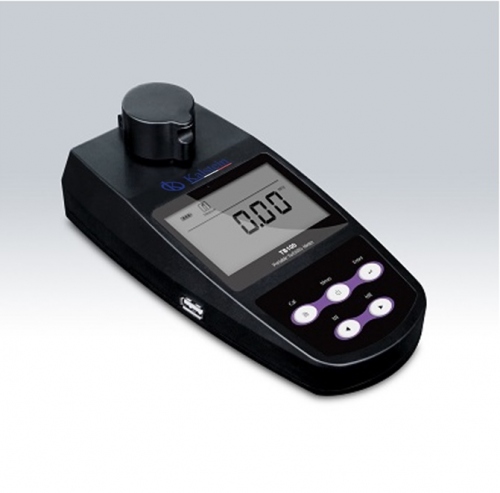

A turbidimeter is an instrument used to measure suspended particles of a liquid or dissolved gas, through an optical analysis, providing reliable and accurate measurements. This equipment is used to detect particles from light sources for ultra pure water and high turbidity applications. There are several models and they are distinguished by the geometric arrangement of the light source with respect to the photo cell.
